|
Sperm anatomy |
|
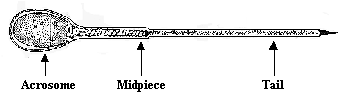 |
|
|
The acrosome contains the
important genetic material (DNA) |
|
|
The midpiece is full of
mitochondria - the power source |
|
|
The tail propels the sperm forward |
|
|
The tail is only to move the sperm into the egg, it is
not intended to swim up the uterus |
|
Major hormones controlling male reproduction |
|
Hormone |
Source |
Controls |
|
Testosterone |
Testes |
Maturation of sperm. Male behaviour.
Male growth
|
|
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) |
Brain |
Production of sperm |
|
Luteinizing
hormone (LH) |
Brain |
Testosterone production |
|
Oxytocin |
Brain |
Ejaculation, pre-coital sexual stimulation |
|
Cortisol |
Adrenal |
Stress hormone has a negative effect |
|
Phases of sexual behaviour |
|
1 |
Courtship |
|
2 |
Mounting |
|
3 |
Active phase where the
boar erects and tries to get the anticlockwise spiral
tip of the penis to lock into the cervix of the sow |
|
4 |
Pre-ejaculation where
the boar starts to thrust |
|
5 |
Production of jelly
from the bulbourethral
glands, which seals the cervix after finishing service.
This is also produced in small amounts throughout the
ejaculation. |
|
6 |
Seminal fluid
production |
|
7 |
Waves of sperm rich
fluid |
|
8 |
Production of more
sperm poor seminal fluids |
|
9 |
Termination of
ejaculation and release of the penis from the cervix |
|
10 |
Dismounting |
|
Factors which may affect libido |
|
|
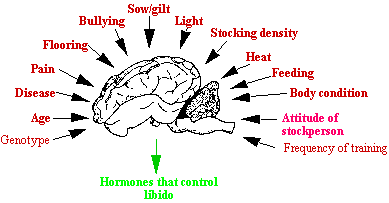
|
